Climate change is now a money-making opportunity.
Yes, you read that right. The world is heating up. Governments and big companies are under pressure to reduce pollution. But they can’t do it alone. So, they buy “carbon credits” from people and businesses who help the environment like those who plant trees or create clean energy projects.
This is called carbon trading and it’s becoming a billion-dollar market.
Key Takeaways
- Carbon trading is a fast-growing, billion-dollar opportunity driven by global climate regulations, ESG goals, and net-zero commitments from corporations and governments.
- Startups can enter the carbon market through multiple paths: launching a carbon trading platform, running green projects, acting as a broker, or combining all models for higher profitability.
- Carbon credits are earned by reducing or removing CO₂ through projects like tree planting, renewable energy, or clean technology initiatives.
- Verified carbon credits hold higher value and trust, making certification through recognized standards essential for long-term success.
- Carbon trading platforms generate scalable revenue through commissions, premium listings, analytics, and verification support.
- Buyers include corporations with net-zero goals, compliance-driven industries, governments, NGOs, and climate investment funds.
- Combining project ownership with platform control gives startups maximum revenue, brand authority, and market influence.
- Strong documentation, verification, transparency, and marketing visibility are critical to winning buyers in the carbon market.
- SEO and digital marketing play a major role in helping carbon startups attract buyers, partners, and investors globally.
Ready to Build a Profitable Carbon Trading Business?
Whether you want to launch a carbon trading platform, start a verified green project, or scale your carbon credit sales, SEO Circular helps you get visibility, buyers, and real revenue.
Book a free carbon business strategy call.
Now, here’s the opportunity:
If you’re a startup, you can enter this business in two big ways:
- Build a carbon credit trading platform or app – like a stock market, but for carbon.
- Start a green project – like planting trees – and sell the carbon credits you earn.
Real Example:
Imagine you plant enough trees to absorb 1,000 tons of CO₂. You earn 1,000 carbon credits. If each credit sells for $10, you just made $10,000.
But how do you sell your carbon credits?
You have two options to earn money from carbon trading:
- Sell on an Existing CTX Platform
You contact any carbon credit exchange or platform (like Gold Standard, Verra, or voluntary platforms). They verify your project and then buy or list your carbon credits for sale. Once sold, you get paid. In this case the platform will charge you a commission fee.
- Launch Your Own Carbon Credit Platform
This is the bigger business model. You can build your own carbon trading platform and:
- Sell your own carbon credits directly
- Invite other farmers, landowners, or green project owners to sell their credits through your platform
- Charge commission or fees on every transaction
This way, your platform becomes a hub for carbon trading — just like a stock exchange, but for environmental impact.
At SEO Circular, we help startups promote both models. Whether you’re launching a green project or a full-scale trading platform, we help you get traffic, leads, partners, and real buyers through smart digital marketing.
What Is Carbon Trading? (Explained Simply)
Let’s explain everything in detail — so even if you’re new, you’ll get it clearly.
Carbon trading is like selling fresh air to people who are polluting too much.
Here’s how it works:
Every company, factory, or airline releases carbon dioxide (CO₂) into the air. But there’s a limit to how much they’re allowed to pollute. If they go beyond that limit, they need to buy carbon credits to make up for the extra pollution.
Now, if you plant trees or run a clean energy project, you’re helping reduce carbon from the air. For that, you earn carbon credits — like reward points.
So, carbon trading means:
- One side is selling carbon credits (people who reduce emissions)
- The other side is buying carbon credits (people who pollute more than allowed)
This creates a carbon market — just like a regular market where goods are bought and sold. Here, carbon credits are the product.
Quick Example:
Let’s say:
- You reduce 500 tons of CO₂
- You earn 500 carbon credits
- A factory needs 500 credits to stay within legal limits
- They buy your credits for $12 each
That’s $6,000 in your pocket — just for running an eco-friendly project. This system rewards people who protect the planet and lets businesses stay compliant with climate rules.
Carbon Credit Business Models for Startups
If you’re a startup planning to enter the carbon credit industry, you have more than one way to make money. Let’s break down the most popular and profitable business models — explained with real examples and startup-friendly language.
Model #1: Start a Carbon Credit Trading Platform (App or Website)
This is like building a stock exchange, but for carbon credits. You create a platform where:
- Project owners (like tree planters or solar farms) list their carbon credits. You can charge for listing their project.
- Buyers (companies, governments, investors) come to buy them
- Also you can charge commission from buyers and sellers for every transaction.
How You Make Money:
Charge commission on every credit sold : Earn a small percentage from every carbon credit transaction made on your platform, just like a marketplace commission model.
Offer verification support or consulting for a fee: Help project owners with carbon credit verification, documentation, and compliance, and charge a service or consulting fee.
Provide premium listing or marketing for sellers: Allow sellers to pay extra to promote their carbon credits, get featured listings, or reach more buyers faster.
Sell platform data analytics or reporting tools : Offer paid access to market insights, pricing trends, emission data, and reports useful for buyers and investors.
Example:
If 10,000 credits are sold on your platform in a month at $10 per credit, and you charge 2% commission: You make: $2,000/month. As volume increases, so does your revenue.
What You Need:
- A website or app (we help with marketing). We have already developed both an app and website. You can buy readymade ones from us.
- Legal approval to operate (depending on country)
- A team to manage listings, compliance, and tech
Bonus Tip: You can also run your own credit projects and sell them on your own platform — keeping 100% profit.
Model #2: Run a Carbon Credit Project (Like Tree Planting)
If you have land or a way to reduce carbon, you can run a carbon project and earn credits yourself.
Common projects include:
- Tree planting (reforestation, agroforestry)
- Solar power or wind farms
- Clean cooking or waste-to-energy systems
How You Make Money:
- Each ton of carbon you reduce = 1 carbon credit
- You sell these credits to platforms or directly to buyers
Example:
You plant trees that absorb 5,000 tons of CO₂ per year.
If each credit sells at $10: You make $50,000/year (minus verification and project costs).
What You Need:
- A valid project with monitoring
- Verification from trusted body (we’ll explain in Section 7)
- A place to sell credits — via platform or your own network
Model #3: Be a Carbon Credit Broker or Aggregator
You don’t need land or a platform — you can be a middleman.
Here’s how:
- Find farmers or small project owners with tree plantations or clean projects
- Help them get verified and listed on carbon markets
- Charge a commission for every sale
This is like real estate agents who help people sell property — but here you sell carbon credits.
Example:
If your farmer client earns $20,000 by selling carbon credits, and you charge 10% commission:
You earn $2,000 just for connecting the dots.
Model #4: Combine Platform + Project
The most powerful model? Do both.
- Start your own tree plantation project
- Build your own platform
- Sell your own credits
- Invite others to list their projects too
Now you’re making money from:
- Selling your own credits
- Platform commission
- Branding and marketing fees
- Partner projects
It’s like owning a farm and the marketplace where all farms sell. Pure profit + full control.
How Carbon Credits Are Created, Verified & Sold
Let’s now break down the entire carbon credit process into easy steps — so you know exactly how to earn and sell carbon credits.
Whether you’re planting trees, setting up a solar farm, or working with farmers — the steps are mostly the same.
Step 1: Start a Green Project That Reduces Carbon
First, you need a project that actually reduces carbon emissions or removes carbon from the atmosphere.
Examples:
- Planting trees on empty land
- Installing solar panels to replace coal energy
- Running clean cookstove programs in rural areas
Every time your project reduces pollution or absorbs CO₂ — you’re creating carbon savings.
Step 2: Measure How Much CO₂ You’re Reducing
You must track and measure your project’s carbon impact.
Example:
If your tree plantation absorbs 1,000 tons of CO₂ in a year, that equals 1,000 carbon credits.
You’ll need basic tools like:
- GPS maps
- Satellite images
- Carbon calculators (available online)
- A consultant (optional but helpful)
Step 3: Get Your Project Verified
This is an important step. To sell credits, your project must be verified by an approved body — like:
- Verra (VCS)
- Gold Standard
- Climate Action Reserve
- Global Carbon Council
They check:
- Is your project real?
- Is the carbon saved measurable?
- Is it long-term and not already claimed?
Once approved, they issue your carbon credits in their system — and you’re ready to sell!
Step 4: Sell Your Carbon Credits
Now comes the fun part — you sell your verified carbon credits for money.
You can sell them in 3 ways:
- On carbon exchanges (like a marketplace)
- Directly to buyers (companies, NGOs, government)
- On your own carbon trading platform (if you built one)
Pro tip: Verified credits sell for more money than unverified ones. Buyers trust certified credits.
Real Example:
Let’s say your project reduces 5,000 tons of CO₂ per year
You get 5,000 verified carbon credits
You sell them at $10 per credit
You earn: $50,000/year
If you do this every year, you’ve built a recurring revenue business — plus you’re helping the planet.
Carbon Credit Creation & Selling Process
| Step | What Happens | Key Output |
| Start Green Project | Trees, solar, clean energy, cookstoves | Carbon reduction begins |
| Measure CO₂ Impact | Track emissions reduced or removed | Carbon data |
| Verification | Third-party verification by standards | Verified credits |
| Credit Issuance | Credits issued on registry | Tradable assets |
| Selling Credits | Exchange, direct buyers, or own platform | Revenue generated |
Buyers in the Carbon Market: Who Pays & Why
If you’re going to sell carbon credits, you need to know who’s buying and what they care about.
Here’s the good news — there’s a growing list of companies and organizations that must or want to buy carbon credits. Why? Because they either:
- Legally have to (compliance)
- Or they voluntarily want to go green (reputation, branding, ESG goals)
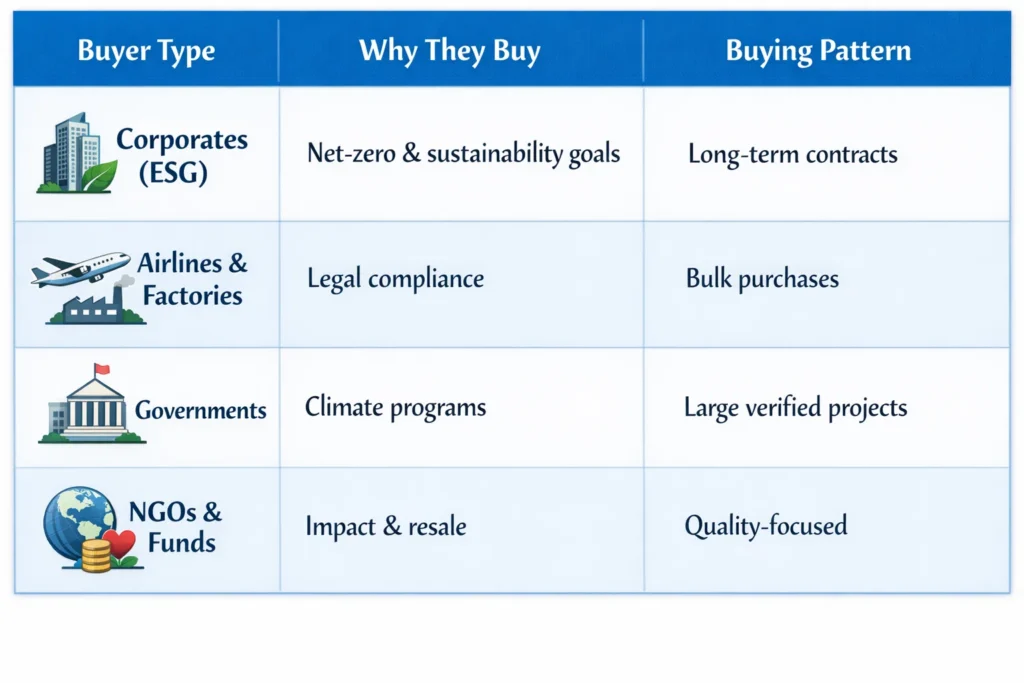
Let’s understand them in detail:
Large Corporations with ESG or Net-Zero Targets
Big brands like Microsoft, Google, Apple, Amazon all have net-zero emission goals. That means they promise to cancel out their carbon footprint.
They still pollute (flights, data centers, deliveries), so to balance that, they buy carbon credits.
These companies want:
- Verified, high-quality credits
- Green projects they can show in reports
- Reliable sellers or platforms
Airlines, Oil Companies & Factories (Compliance Buyers)
Some industries are required by law to limit emissions. If they go over the legal cap, they must buy carbon credits.
Example buyers:
- Airlines (international flights)
- Oil & gas companies
- Cement, steel, and coal-based factories
These buyers often purchase in bulk and care more about price and volume.
Governments and Public Sector Programs
Some governments support green goals through:
- National carbon offset programs
- Buying credits for climate funds
- International climate partnerships
They usually buy from large projects or verified registries and offer long-term contracts.
NGOs, Climate Funds & Carbon Brokers
Some climate-focused NGOs and investment funds buy carbon credits to:
- Support eco-projects
- Resell at higher value
- Help communities go green
These buyers look for impact + quality, not just numbers.
Why Do They Pay?
- To avoid fines (compliance buyers)
- To improve brand image (corporate buyers)
- To attract investors with ESG goals
- To fulfill global climate commitments
What This Means for You
If you run a carbon project or own a platform:
- Target the right buyer for your model
- Use SEO and marketing to get discovered online
- Show transparency and verification to earn trust
Revenue Models in Carbon Trading (With Examples & Calculations)
If you’re entering the carbon market, you have multiple ways to earn. Whether you’re planting trees, building a solar farm, or launching a carbon credit trading platform, there’s real profit potential.
Let’s break down each revenue model one by one:
Model #1: Selling Carbon Credits from Your Own Green Project
If you run a project like tree planting, clean cookstoves, or renewable energy — you earn carbon credits based on how much CO₂ you reduce.
Example:
- You plant trees that reduce 5,000 tons of CO₂ per year
- You get 5,000 carbon credits
- If market price = $10 per credit
You earn $50,000/year
You can increase revenue by:
- Expanding the project (more land, more trees)
- Getting premium verification (some buyers pay more)
- Selling directly to buyers (to avoid middlemen)
Model #2: Commission from a Carbon Credit Trading Platform
If you launch a carbon exchange platform, you earn money by:
- Charging transaction fees (like 1-5% per trade)
- Offering premium listings or promotions
- Selling analytics or reporting tools
- Providing verification support for new sellers
Example:
- 20,000 credits are sold monthly
- Average price = $12 per credit = $240,000 trade volume
- Your platform charges 2% commission
You earn $4,800/month
As volume increases, your income scales fast — and you don’t need to own any projects yourself.
Model #3: Aggregator/Broker Commission
If you connect farmers or small project owners to buyers or platforms, you act as a broker. You help them get verified and listed.
Example:
- Farmer sells 3,000 credits at $10 = $30,000
- You take 10% commission = $3,000 profit (no project cost!)
You can work with multiple farmers or NGOs, and scale this without owning land or assets.
Model #4: Combine All for Maximum Profit
Smart startups combine models for full control.
Example:
- You start a tree planting project (Model 1)
- You build a trading platform (Model 2)
- You let other farmers list their credits on your platform (Model 3)
Now, you’re making money from:
- Selling your own credits
- Platform commissions
- Partner credit listings
It’s like owning both the farm and the market — you win from every angle.
Revenue Sources in a Carbon Trading Business
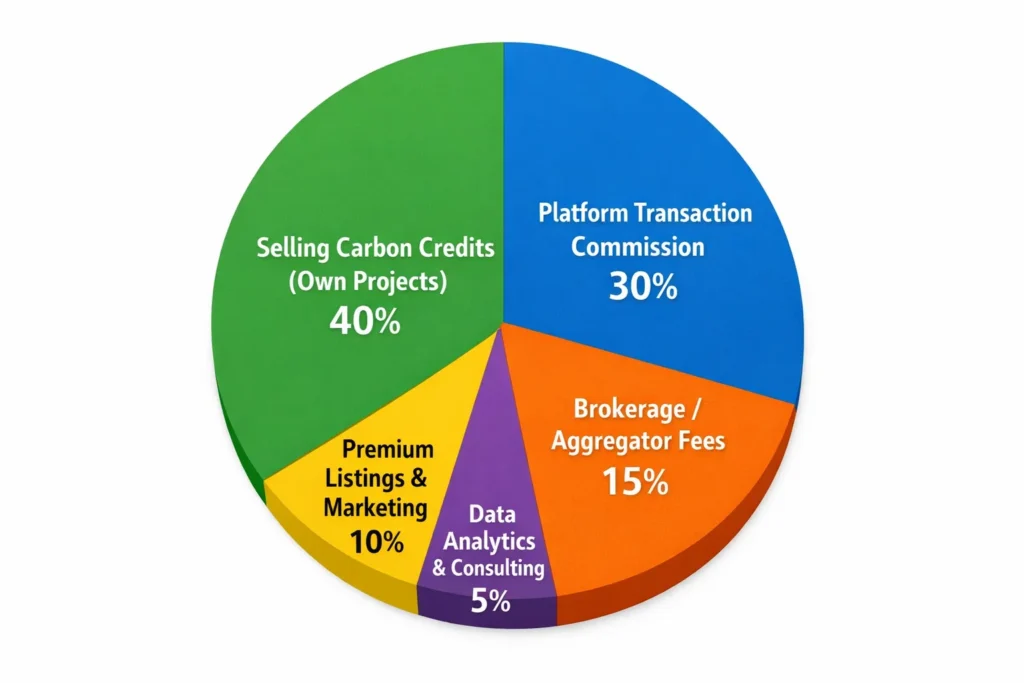
Selling carbon credits (40%) is the main revenue source, especially from owned green projects like tree planting or renewable energy.
Platform transaction commissions (30%) generate recurring income as buyers and sellers trade credits on the platform.
Brokerage or aggregator fees (15%) come from helping project owners connect with buyers and complete verified sales.
Premium listings and marketing (10%) allow sellers to pay for better visibility and faster deal closures.
Data analytics and consulting (5%) provide added value through reports, insights, and advisory services.
Legal & Verification Process Made Simple
Before you can sell carbon credits, your project must go through a verification process. This is how you prove that your project is real, measurable, and actually reducing or removing carbon from the atmosphere.
Think of it like getting a product certified before selling it to the public.
Step 1: Choose the Right Type of Market
There are two types of carbon markets:
Voluntary Market
- You choose to sell credits without legal pressure
- Buyers include corporations, NGOs, ESG investors
- Most startups and green projects begin here
- Easier to enter, fewer regulations
Compliance Market
- Governments require companies to offset emissions
- Requires strong documentation and legal approvals
- Good for large-scale industrial projects
Tip: As a startup, it’s easier and faster to start in the voluntary market.
Step 2: Select a Verified Standard
A standard is an organization that checks your project, calculates your carbon savings, and issues the official carbon credits.
Top verification bodies include:
- Verra (VCS) – Most widely used
- Gold Standard – High-quality, trusted for climate and community impact
- Global Carbon Council – Popular in MENA region
- Climate Action Reserve – Mainly U.S.-focused
Each has its own rules, documents, and fees. You’ll need to follow their methodology based on your project type (forestry, energy, agriculture, etc.)
Step 3: Monitor, Measure, and Document
You must keep proper data to prove your project’s impact:
- GPS maps or satellite images of land
- Tree species and growth data (for plantations)
- Energy savings (for solar, clean cookstoves, etc.)
- Proof of additionality (your project wouldn’t happen without carbon finance)
Some tools can help — or you can hire a carbon project consultant.
Step 4: Hire a Third-Party Verifier
The chosen standard will send an independent verifier to check your data. This is a professional body that:
- Visits your project (sometimes virtually)
- Reviews your documents
- Confirms your carbon savings
Once verified, the credits are issued in your name.
Step 5: Register and Sell Credits
After verification, your credits are live on the registry. You can:
- List them on your own platform
- Sell to companies or brokers
- Partner with existing exchanges
Now your credits are legally valid and sellable — just like gold with a certificate.
Estimated Startup Cost for Carbon Trading Business
| Business Model | Cost Category | Estimated Cost Range | What This Includes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Credit Project (Tree, Solar, Clean Energy) | Project setup & operations | $10,000 – $50,000 | Land access or partnerships, planting or installation, monitoring |
| Verification & certification | $5,000 – $20,000 | Verification by standards like Verra or Gold Standard | |
| Monitoring & reporting | $2,000 – $5,000 / year | Data tracking, satellite images, documentation | |
| Carbon Trading Platform (App / Website) | Platform development (MVP) | $15,000 – $40,000 | Website or app, dashboards, basic trading features |
| Legal & compliance setup | $3,000 – $10,000 | Business registration, legal approvals, policies | |
| Hosting & maintenance | $1,000 – $3,000 / year | Server, security, updates | |
| Marketing & user acquisition | $2,000 – $8,000 / month | SEO, content, ads, outreach | |
| Broker / Aggregator Model | Verification support & onboarding | $1,000 – $3,000 | Documentation help, consultant fees |
| Sales & marketing | $1,000 – $2,000 | Outreach, lead generation | |
| Total starting cost | Under $5,000 | Low-risk entry model | |
| Hybrid Model (Platform + Project) | Combined investment | $30,000 – $80,000+ | Project costs + platform + marketing |
How to Start a Carbon Trading Platform or Project
Now that you understand the models, the buyers, and the verification process — it’s time to launch. Whether you’re starting a carbon trading platform or running a tree planting or clean energy project, here’s a simple action plan to get you moving.
A. How to Start a Carbon Credit Platform (App or Website)
If you want to build a carbon credit marketplace, here’s what you need:
Step 1: Finalize Your Platform Idea
Decide:
- Will your platform allow others to list and sell carbon credits?
- Will you also sell your own credits?
- Will you charge commission, listing fees, or offer extra services?
Tip: Start simple — basic buying/selling. Add more features later.
Step 2: Build the Platform (MVP First)
You don’t need to build a massive app from Day 1. You can launch an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) — a simple website or app that allows:
- Sellers to register and list projects
- Buyers to browse and buy
- Admin dashboard to manage trades
Use a web development agency or hire developers. Focus on:
- Secure login
- Payment integration
- Project listing
- Credit tracking system
Step 3: Get Legal & Verification Ready
If your platform also supports verification or registration:
- Learn the process from Verra or Gold Standard
- Build a partner network with carbon consultants
- Create a project submission form for sellers
Step 4: Attract Sellers and Buyers
This is where SEO Circular comes in:
- We run digital marketing campaigns to bring project owners and buyers to your platform
- We use SEO, PPC, content, social media, and more to grow traffic and trust
B. How to Start a Carbon Credit Project (Tree Planting, Solar, etc.)
If you want to generate and sell your own credits, here’s your path:
Step 1: Pick a Project Type
Choose what works for you:
- Tree planting (great for landowners or farmer networks)
- Renewable energy (solar/wind for rural areas)
- Clean cookstoves or biogas units
Step 2: Choose Your Location & Partners
If you don’t have land or resources yourself, partner with:
- Local farmers
- Landowners
- NGOs
Create a simple agreement that says you’ll manage the carbon credit side and share profit.
Step 3: Document Everything
Start tracking from day one:
- Area covered
- Type of project (trees, energy, etc.)
- Tools or tech used
- Pictures, GPS maps, reports
This is needed later for verification.
Step 4: Apply for Verification
Choose a registry (like Gold Standard or Verra), follow their steps, and get your credits verified. You can do it yourself or hire a consultant.
Step 5: Sell Your Credits
Once verified, you can:
- Sell to brokers
- List on existing exchanges
- Or better — sell on your own platform
How SEO Circular Helps You Succeed in the Carbon Market
Starting a carbon credit project or platform is smart. But without visibility, buyers and investors won’t find you. That’s where SEO Circular comes in — your digital marketing partner in the green economy.
We don’t just run ads. We build your brand, visibility, and trust in the carbon market.
FAQs
Voluntary markets allow businesses to offset emissions by choice, while compliance markets are regulated by governments and legally require companies to offset emissions.
Carbon credit prices vary based on project type, quality, and verification, but typically range between $5 and $30 per credit in voluntary markets.
Verification can take several months depending on project type, documentation quality, and the chosen verification body.
Major buyers include large corporations with ESG goals, airlines, oil and gas companies, manufacturers, governments, NGOs, and climate funds.